Portal:Africa



Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent after Asia. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 20% of Earth's land area and 6% of its total surface area. With nearly 1.4 billion people as of 2021, it accounts for about 18% of the world's human population. Africa's population is the youngest among all the continents; the median age in 2012 was 19.7, when the worldwide median age was 30.4. Based on 2024 projections, Africa's population will exceed 3.8 billion people by 2100. Africa is the least wealthy inhabited continent per capita and second-least wealthy by total wealth, ahead of Oceania. Scholars have attributed this to different factors including geography, climate, corruption, colonialism, the Cold War, and neocolonialism. Despite this low concentration of wealth, recent economic expansion and a large and young population make Africa an important economic market in the broader global context, and Africa has a large quantity of natural resources.
Africa is highly biodiverse; it is the continent with the largest number of megafauna species, as it was least affected by the extinction of the Pleistocene megafauna. However, Africa is also heavily affected by a wide range of environmental issues, including desertification, deforestation, water scarcity, and pollution. These entrenched environmental concerns are expected to worsen as climate change impacts Africa. The UN Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change has identified Africa as the continent most vulnerable to climate change.
The history of Africa is long, complex, and varied, and has often been under-appreciated by the global historical community. In African societies the oral word is revered, and they have generally recorded their history via oral tradition, which has led anthropologists to term them "oral civilisations", contrasted with "literate civilisations" which pride the written word. African culture is rich and diverse both within and between the continent's regions, encompassing art, cuisine, music and dance, religion, and dress.
Africa, particularly Eastern Africa, is widely accepted to be the place of origin of humans and the Hominidae clade, also known as the great apes. The earliest hominids and their ancestors have been dated to around 7 million years ago, and Homo sapiens (modern human) are believed to have originated in Africa 350,000 to 260,000 years ago. In the 4th and 3rd millennia BCE Ancient Egypt, Kerma, Punt, and the Tichitt Tradition emerged in North, East and West Africa, while from 3000 BCE to 500 CE the Bantu expansion swept from modern-day Cameroon through Central, East, and Southern Africa, displacing or absorbing groups such as the Khoisan and Pygmies. Some African empires include Wagadu, Mali, Songhai, Sokoto, Ife, Benin, Asante, the Fatimids, Almoravids, Almohads, Ayyubids, Mamluks, Kongo, Mwene Muji, Luba, Lunda, Kitara, Aksum, Ethiopia, Adal, Ajuran, Kilwa, Sakalava, Imerina, Maravi, Mutapa, Rozvi, Mthwakazi, and Zulu. Despite the predominance of states, many societies were heterarchical and stateless. Slave trades created various diasporas, especially in the Americas. From the late 19th century to early 20th century, driven by the Second Industrial Revolution, most of Africa was rapidly conquered and colonised by European nations, save for Ethiopia and Liberia. European rule had significant impacts on Africa's societies, and colonies were maintained for the purpose of economic exploitation and extraction of natural resources. Most present states emerged from a process of decolonisation following World War II, and established the Organisation of African Unity in 1963, the predecessor to the African Union. The nascent countries decided to keep their colonial borders, with traditional power structures used in governance to varying degrees. (Full article...)
Selected article –

The Congo Crisis (French: Crise congolaise) was a period of political upheaval and conflict between 1960 and 1965 in the Republic of the Congo (today the Democratic Republic of the Congo). The crisis began almost immediately after the Congo became independent from Belgium and ended, unofficially, with the entire country under the rule of Joseph-Désiré Mobutu. Constituting a series of civil wars, the Congo Crisis was also a proxy conflict in the Cold War, in which the Soviet Union and the United States supported opposing factions. Around 100,000 people are believed to have been killed during the crisis.
A nationalist movement in the Belgian Congo demanded the end of colonial rule: this led to the country's independence on 30 June 1960. Minimal preparations had been made and many issues, such as federalism, tribalism, and ethnic nationalism, remained unresolved. In the first week of July, a mutiny broke out in the army and violence erupted between black and white civilians. Belgium sent troops to protect fleeing white citizens. Katanga and South Kasai seceded with Belgian support. Amid continuing unrest and violence, the United Nations deployed peacekeepers, but UN Secretary-General Dag Hammarskjöld refused to use these troops to help the central government in Léopoldville fight the secessionists. Prime Minister Patrice Lumumba, the charismatic leader of the largest nationalist faction, reacted by calling for assistance from the Soviet Union, which promptly sent military advisers and other support. (Full article...)
Featured pictures –
Did you know (auto-generated) -

- ... that nursing educator Helen Turner Watson was one of the first African-American women to become a commissioned officer in the United States Navy?
- ... that in 1888, Edward P. Duplex became the first African American to be elected a mayor in California?
- ... that American Olympic rugby player Sarah Levy is the great-granddaughter of a Springbok?
- ... that Pocatello mayor Les Purce was the first African-American political officeholder in Idaho?
- ... that scientists tested the age of an African termite's inhabited mound—and found it to be 34,000 years old?
- ... that goalkeeper Sophie Whitehouse, who has lived in England, Africa and the US, has been chosen to play soccer for the Republic of Ireland?
Categories
Selected biography –
Dutty Boukman (or Boukman Dutty; died 7 November 1791) was a leader of the Haitian Revolution. Born to a Muslim family in Senegambia (present-day Senegal and Gambia), he was enslaved to Jamaica. He eventually ended up in Haiti, where he became a leader of the Maroons and a vodou houngan (priest).
According to some contemporary accounts, Boukman, alongside Cécile Fatiman, a Vodou mambo, presided over the religious ceremony at Bois Caïman, in August 1791, that served as the catalyst to the 1791 slave revolt which is usually considered the beginning of the Haitian Revolution. (Full article...)
Selected country –
 |
 |
|
| ||
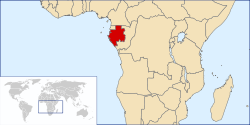
Gabon, or the Gabonese Republic, is a country in west central Africa. It borders on Equatorial Guinea, Cameroon, the Republic of the Congo and the Gulf of Guinea. Since its independence from France on August 17, 1960, the Republic has been ruled by only two autocratic presidents; the incumbent El Hadj Omar Bongo Ondimba has been in power since 1967 and is currently Africa's longest-serving head of state. Gabon introduced a multiparty system and a new democratic constitution in the early 1990s that allowed for a more transparent electoral process and for reforms of governmental institutions.
Gabon has at least forty ethnic groups with separate languages and cultures, of which the Fang are generally thought to be the largest. A small population, abundant natural resources (including offshore petroleum reserves), and foreign private investment have helped make Gabon one of the most prosperous countries in the region, with a per capita income of four times the average for Sub-Saharan Africa, although the distribution of income from this industry is extremely unequal. (Read more...)
Selected city –

Niamey (French pronunciation: [njamɛ]) is the capital and largest city of Niger. Niamey lies on the Niger River, primarily situated on the east bank. Niamey's population was counted as 1,026,848 as of the 2012 census. As of 2017, population projections show the capital district growing at a slower rate than the country as a whole, which has the world's highest fertility rate. The city is located in a pearl millet growing region, while manufacturing industries include bricks, ceramic goods, cement, and weaving. (Full article...)
In the news
- 16 April 2025 – Somali Civil War
- Al-Shabaab militants capture the Adan Yabal District in Middle Shabelle, Somalia, as the group continues to advance towards the capital Mogadishu. (Reuters)
- 16 April 2025 –
- A boat carrying around 400 people catches fire and capsizes on the Congo River near Mbandaka, Democratic Republic of the Congo, killing at least 50 people and leaving hundreds more missing. (AP)
- 16 April 2025 – Sudanese civil war
- The leader of the Sudanese Rapid Support Forces, Mohamed Hamdan Dagalo, announces the establishment of the Government of Peace and Unity, a rival government to the country's armed forces. (BBC News)
- 15 April 2025 – Sudanese civil war, Foreign aid to Sudan
- Humanitarian impact of the Sudanese civil war
- The European Union and its member states pledge €522 million (US$590 million) and the United Kingdom pledges £120 million (US$141 million) in humanitarian aid to Sudan to deliver food and supplies to over 650,000 internally displaced Sudanese people affected by the fighting between the Rapid Support Forces and the Sudanese Armed Forces. The two groups also call for an immediate ceasefire to end the war. (DW) (AP)
- 15 April 2025 – Algeria–France relations
- France expels twelve Algerian diplomatic officials from the country after Algeria expelled twelve French officials yesterday over the arrest of an Algerian consular official in a kidnapping case. France also recalls its ambassador from Algiers. (AP) (Bloomberg)
Updated: 5:05, 17 April 2025
General images -
Africa topics
More did you know –

- ...that the 1459 Fra Mauro map (pictured) reports that "a junk from India" rounded the Cape of Good Hope in 1420, around 70 years before the navigations of Vasco da Gama?
- ...that the 1998 Sudan famine was caused by human rights abuses in the midst of the Second Sudanese Civil War?
- ...that a smokie is a West African delicacy made by blowtorching the carcass of a sheep or goat without removing its fleece?
- ...that Anne-Marie Nzié, a Cameroonian bikutsi singer, dedicated the song Liberté to President Paul Biya and his party, the Cameroon People's Democratic Movement?
Related portals
Major Religions in Africa
North Africa
West Africa
Central Africa
East Africa
Southern Africa
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikispecies
Directory of species -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wikivoyage
Free travel guide -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus